 The growing increase in the number of the students in the Southern provinces that reached ? is considered an indicator testifying to the importance that the State attaches to the educational sector, so much so as the number of students did not exceed a few hundreds back in 1975.
The growing increase in the number of the students in the Southern provinces that reached ? is considered an indicator testifying to the importance that the State attaches to the educational sector, so much so as the number of students did not exceed a few hundreds back in 1975.
On the other hand, this huge rise in the number of students reflects the effective efforts and plans of the Moroccan government in the educational field in the Southern provinces since they regained independence. Out of concern for sustainable development in education, the Moroccan government has made sure the educational system is in sync with the deeply-ingrained Islamic values and traditions, which represent a strong bond that ties the different Sahara tribes to the whole Moroccan community throughout Morocco.
On the grounds of these major objectives, Arabic is used as the teaching vehicle and all curricula and syllabi have been unified. Besides, the Moroccan authorities have insisted since the return of the Southern territories to Morocco on providing a seat to each single pupil aged six. This initiative has required the sustained intervention on the State in view of the increasing number of students at this age group.
The right to education has also been speeded up in good conditions so as to allow the children at schooling age to join schools, and also to allow the youth who have never enrolled or have dropped out to have access to vocational training.
Thanks to this training, the Southern provinces have been able to meet the local needs in terms of qualified staff to implement the plans of sustainable human development. In order to reach the objectives of the educational sector, a lot of efforts have been made to upgrade the infrastructure and put in the huge necessary human and material resources. The broad lines of this operation included the construction of schools, the provision of equipment and the guaranteeing of equal opportunities in education.
The educational sector in Laayoune:
Table showing educational institutions
Public sector:
|
Cycles |
Number of institutions |
Number of students |
Teaching staff |
|
Fundamental Education |
47 |
27.179 |
835 |
| Junior secondary school |
11 |
13.313 |
480 |
| Total |
58 |
40.492 |
1.315 |
| Qualifying secondary school |
07 |
6.732 |
324 |
| Overall total |
65 |
47.224 |
1.639 |
The private sector:
|
Type of education |
Number |
| Traditional education |
21 |
| Modern education |
154
|
| Total |
175 |
Distribution of students per areas
|
Areas |
Overall number of students |
Percentage of girls in the overall number |
| Urban areas |
6931 |
3224
|
| Rural areas |
174 |
66 |
| Total |
7105 |
3290 |
Education in Oued-Eddahab- Lagouira Region
1- Primary education in the public and private sectors
The number of pupils enrolled in Oued-Eddahab- Lagouira Region in primary education in both the public and the private sectors for the year 2002-2003 reached 9094, that is an increase of 8%. The following tables present the distribution of students per sex and age as well as the percentage of schooling.
Table presenting numbers of students par age in the region (public and private sectors)
|
Type of education |
Cycle |
Number of students |
Number of students |
Number of students |
|
|
Male |
Female |
Total |
|
Primary |
4569 |
4284 |
8853 |
|
Primary |
134 |
107 |
241 |
| Total |
|
4703 |
4391 |
9094 |
Table presenting students per sex in the rural areas
|
|
2002-2003
|
|
|
| Type of education |
Cycle |
Male |
Female |
Total |
| Public |
Primary |
55 |
57 |
112 |
Table presenting schooling rates
|
Age group |
Percentage |
6 years
|
96 |
| 6 - 11 years |
97 |
2- Junior secondary school
3- The number of pupils enrolled in the Junior secondary school in the Oued-Eddahab- Lagouira Region for the year 2003-2004 2164 pupils, that is an increase of 5%. The number of girls reached 955, that is an increase 6%. The rate of schooling of the 12-14 years age group amounted to 59%.
Table showing the trend of the students in the junior secondary level per sex:
|
Sex |
2001-2002 |
2002-2003 |
| Male |
1156 |
1209 |
| Female |
904 |
955 |
| Total |
2060 |
2164 |
 4- Qualifying secondary education
4- Qualifying secondary education
The general and technical qualifying secondary education is an important part of the educational system because it the transitional period between the junior secondary and the university level. It prepares the students to both better pursue their studies and better integrate the job market.
The number of the students in the qualifying secondary education with all its kinds (general and original) has reached 1306, that is an increase of 14% compared to the figures of the academic year 2001-2002. Depending on the type of education, there are 1256 students in the general education and 50 students in the original one. The number of classes in this cycle amounts to 39.
Table showing the trend of the students in the qualifying secondary level per sex:
|
Sex |
2001-2002 |
2002-2003 |
| Male |
615 |
710 |
| Female |
530 |
596 |
| Total |
1145 |
1306 |
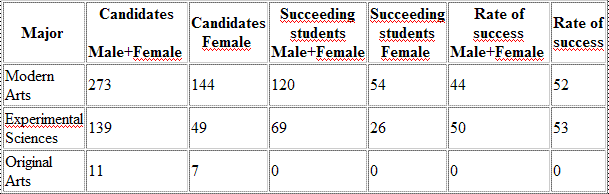
On the other hand, the number of candidates for the baccalaureate exam in the second year across the board has reached 423. The rate of success was around 45%, that is 189 students. The following table shows the results as well as the rate of success per major.
Table of the baccalaureate results per major and sex , June 2003
Education in Goulmim-Smara Region:
As development is hard to achieve in an illiterate society, a lot of emphasis has been put mainly on the educational sector. In view of the huge deficiency that could be witnessed in this sector upon the return of these region to mainland, because the whole infrastructure at that point in time in 1975 was no more than two rooms in the deteriorated building with no more than 65 students, while the overall number of students today has reached11,501.
The educational policy of the State has been geared sine 1975 towards providing a seat to each pupil at schooling age; to reach this objective, a lot of human and material resources have raised to lay the foundations of an education that keeps with the aspirations and meets the educational and cultural needs.
Primary education
|
|
2004/2005 |
2005/2006 |
Growth rate % |
| Number of institutions |
774 |
738 |
1.14 |
| Number of rooms |
811 |
830 |
2.29 |
| Number of pupils enrolled |
19007 |
18771 |
-1.25 |
| Number of rooms |
831 |
830 |
-0.12 |
Number of teachers
|
835 |
832 |
-0.36 |
General primary education
| |
2004/2005 |
|
2005/2006 |
|
Growth rate% |
|
Total |
Rural |
Total |
Rural |
|
| institutions |
156 |
85 |
158 |
87 |
1.27 |
| Pupils |
71260 |
24834 |
69766 |
24414 |
-2.14 |
| Rooms |
2585 |
1215 |
2581 |
1214 |
-0.15 |
| Teachers |
2807 |
1269 |
2965 |
1268 |
5.32 |
|
2004/2005 |
|
2005/2006 |
|
Growth rate% |
|
Total |
Rural |
Total |
Rural |
|
| institutions |
6 |
0 |
8 |
0 |
25 |
| Pupils |
1064 |
0 |
1297 |
0 |
18 |
| Rooms |
53 |
0 |
59 |
0 |
10.16 |
| Teachers |
66 |
0 |
69 |
0 |
4.34 |
Public Junior secondary education
|
2004/2005 |
|
2005/2006 |
|
Growth rate% |
|
Total |
Rural |
Total |
Rural |
|
| institutions |
33 |
8 |
36 |
8 |
8.33 |
| Pupils |
28422 |
5607 |
30589 |
6324 |
7.08 |
| Rooms |
725 |
158 |
790 |
169 |
8.22 |
| Teachers |
1252 |
269 |
1225 |
250 |
2.20 |
Private Junior secondary education
|
2004/2005 |
|
2005/2006 |
|
Growth rate% |
|
Total |
Rural |
Total |
Rural |
|
| institutions |
1 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
| Pupils |
60 |
0 |
83 |
0 |
28.75 |
| Rooms |
4 |
0 |
5 |
0 |
2 |
| Teachers |
10 |
0 |
12 |
0 |
16.66 |
Public qualifying secondary education
|
2004/2005 |
|
2005/2006 |
|
Growth rate% |
|
Total |
Rural |
Total |
Rural |
|
| institutions |
21 |
4 |
22 |
4 |
4.54 |
| Pupils |
14554 |
1428 |
15435 |
1711 |
5.7 |
| Rooms |
376 |
45 |
410 |
51 |
8.29 |
| Teachers |
775 |
85 |
673 |
60 |
-0.5 |